Acetaldehyde
- the Amalgam Link
|
What is acetaldehyde ?
Acetaldehyde,
also known as ethanal, is an organic chemical
compound. It is an aldehyde that is more toxic
than ethanol and is responsible for many hangover
symptoms in alcohol drinkers. So it is usually
associated with alcohol toxicity.
What
does it have to do with the oral cavity ?
Apart
from the fact that alcohol is usually taken as a
drink. Acetaldehyde is also a toxin associated
with the mycelial fungal form of Candida Albicans
which is associated with inflammatory bowel
disease, gut dysbiosis, leaky gut and nutrients
malabsorption. Candida Albicans is quite
resistant to the effects of mercury, which is a
bactericidal metal. In individuals with amalgams,
there is an increase risk of developing a gut
dysbiosis, an imbalance in the microbial flora of
the gut characterized by an overgrowth of Candida
Albicans in it's mycelial fungal form.
This
gut flora imbalance has many implications
including an increase in acetaldehyde in the
body. Acetaldehyde can affect the metabolic,
neurological, endocrine and immune systems of the
body. Acetaldehyde
may directly inhibit the osteoblastogenic
potential of the bone marrow, and this effect may
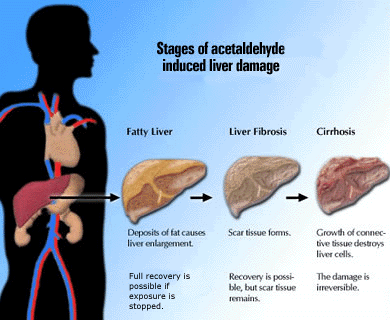
contribute to decreased bone formation and osteoporosis. Acetaldehyde
can also cause damage to the liver which is
usually proportional to the level and length of
exposure.
Thus acetaldehyde has the
potential to impair detoxification and bone
repair thereby impacting issues like oral
osteoporosis, heavy metal toxicity and microbial
toxicity related to oral infections such as gum
diseases, dental and jawbone infections.
|