Problems
related to the bone tissue
|
The maxillofacial bones, including
the upper and lower jaws, are complex structures
made of numerous different tissues. The external
shell is called cortical bone while the internal
portion is called cancellous or trabecular bone.
The bone marrow, with its numerous cell types, is
located within the non-calcified spaces of the
cancellous bone.
Needless
to say bone marrow plays a vital role in the
immune system so any damage to it can have an
adverse effect on your health. There are two
types of bone marrow, red and yellow. The yellow
type which is present in the facial bones has a
higher content of fat cells so is a potential
" deep storage " area for toxins which
are, by nature, fat soluble.
The
jaw bones themselves are the supporting structure
for the teeth and all the soft tissues including
the muscles, gums and skin, allowing you to
speak, chew , swallow ect.... They also are the
only bones containing one the the 12 cranial
nerves coming out of the brain through the skull.
So the maxillofacial bones clearly have an
important role to play in human health.
A
number of disorders can affect the calcified
portion or/and the bone marrow portion of the
maxillofacial bones not including dental problems
themselve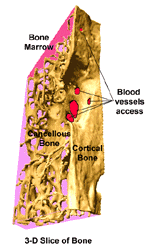 s and trauma induced
damages such as fractures or electrocutions. s and trauma induced
damages such as fractures or electrocutions.
Ref: Histology of Chronic
Ischaemic Bone Disease
|

